How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into every aspect of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll cover essential controls, camera operation, battery management, and legal considerations to ensure you’re prepared for a successful and responsible flight experience.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available online; for example, check out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone to improve your skills. Mastering these techniques ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a rewarding flying experience.
Whether you’re a beginner taking your first steps into the world of drones or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence you need.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, and for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. From there, practice in a safe, open area is key to mastering the skills needed for confident and responsible drone operation.
Understanding the nuances of drone flight involves more than just pushing buttons; it requires a thorough understanding of safety regulations, proper handling techniques, and the ability to adapt to various situations. This guide breaks down the complexities into manageable steps, providing clear explanations and practical advice to help you navigate the exciting world of aerial technology responsibly and confidently.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s physical components, verifying battery levels, and confirming compliance with local regulations. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and legal issues.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone is in optimal condition. The following table Artikels critical checks and their pass/fail criteria.
| Component | Check | Pass | Fail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or wear | No damage, securely fastened | Damage present, loose or missing propellers |
| Motors | Check for free spinning and smooth operation | Motors spin freely without noise or resistance | Motors jammed, making unusual noises, or not spinning |
| Gimbal | Verify gimbal movement and stability | Smooth, stable movement in all directions | Gimbal jerky, unstable, or making unusual noises |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Sufficient charge, no visible damage | Low charge, swollen battery, or visible damage |
| GPS | Confirm GPS signal acquisition | GPS signal locked, sufficient satellites | Weak or no GPS signal |
| Camera | Test camera functionality | Camera operates correctly, image preview clear | Camera malfunctioning, no image preview |
| Airframe | Inspect for damage or loose parts | No visible damage, all parts securely fastened | Damage to airframe, loose parts |
Regulatory Compliance and Airspace Restrictions
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations and airspace restrictions is paramount. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges. Always check the relevant authorities’ websites (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) for specific rules in your area. Examples of potential consequences include flight restrictions near airports, mandatory registration, and limitations on flight altitude and distance.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to react in emergency situations is vital. In case of a malfunction, such as motor failure or GPS signal loss, immediately prioritize a safe landing. If a loss of signal occurs, engage the return-to-home (RTH) function if available, or attempt to manually regain control. Always have a backup plan and prioritize safety over recovering the drone.
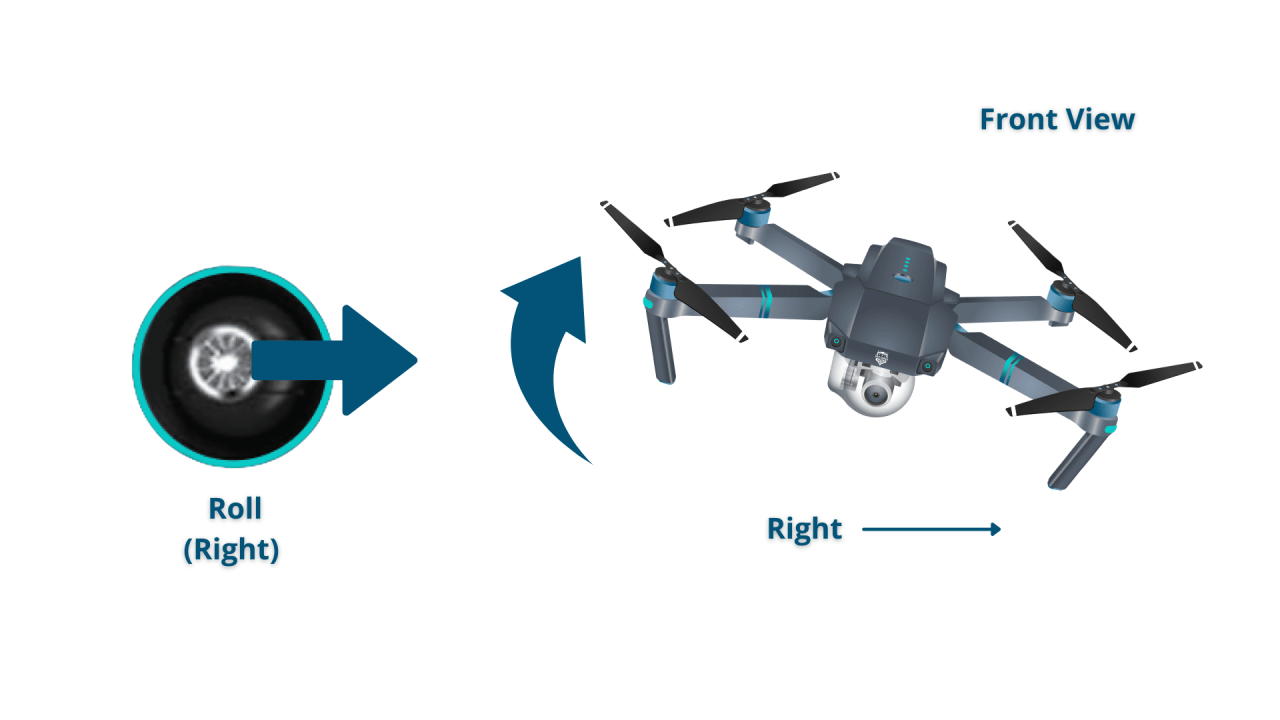
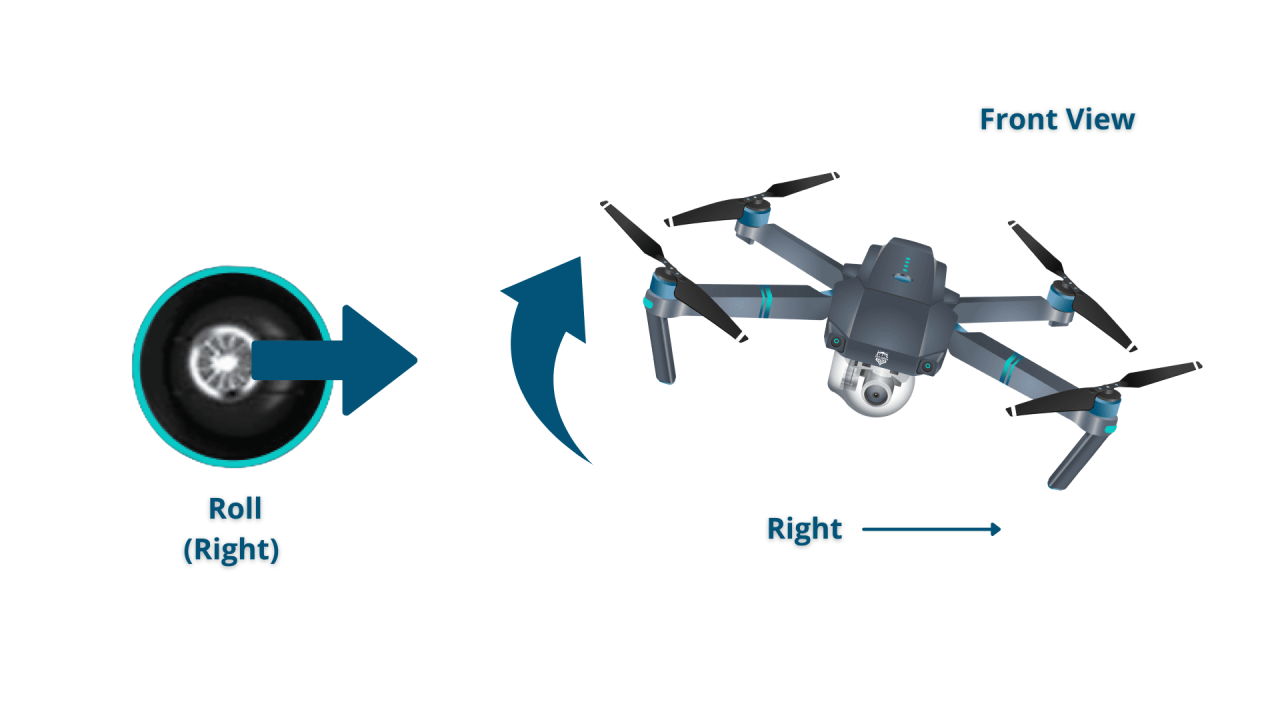
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and efficient operation. This involves understanding the various flight modes, maneuvering techniques, and the different control methods available.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures

Safe takeoff and landing are fundamental aspects of drone operation. Follow these steps for a smooth and controlled flight.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Ensure propellers are clear.
- Slowly lift the drone vertically.
- Hover at a safe altitude.
- For landing, slowly descend vertically.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer various flight modes, each with specific capabilities and limitations. Common modes include Position (GPS-based positioning), Altitude Hold (maintaining a consistent altitude), and Sport (more agile and responsive control). Understanding the limitations of each mode is essential for safe operation.
Drone Maneuvering Techniques
Effective drone maneuvering involves precise hovering, smooth transitions between altitudes and directions, and accurate positioning. The following table compares different control methods.
| Control Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Joystick | Precise control, familiar interface | Can be challenging for beginners |
| App-based controls | Intuitive interface, easy to learn | Less precise control than joysticks |
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality images and videos requires understanding drone camera settings and various shooting techniques. This section covers adjusting camera settings, achieving different camera angles, and transferring captured media.
Camera Settings and Adjustments

Optimizing camera settings is crucial for high-quality footage. The settings will depend on the lighting conditions and the desired outcome. Adjustments should be made according to the scene and desired aesthetic.
- ISO: Adjusts the camera’s sensitivity to light (higher ISO for low-light, lower ISO for bright light).
- Shutter Speed: Controls how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light (faster shutter speed for freezing motion, slower shutter speed for motion blur).
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening (wider aperture for shallower depth of field, narrower aperture for greater depth of field).
- White Balance: Adjusts the color temperature to ensure accurate color representation.
- Exposure Compensation: Fine-tunes the overall brightness of the image.
Camera Angles and Shots
Experiment with different camera angles to achieve diverse and visually appealing shots. Techniques include aerial shots, close-ups, and tracking shots. Understanding the drone’s capabilities will allow for creative and dynamic cinematography.
Media Transfer and Management
After capturing media, transfer it to a computer or other device for editing and storage. Use the appropriate software and cables provided with your drone for efficient and safe transfer. Organize your files for easy access and backup.
Drone Battery Management and Flight Time
Proper battery management is vital for extending the lifespan of your drone batteries and ensuring safe operation. This involves understanding charging procedures, storage recommendations, and factors influencing flight time.
Battery Best Practices
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging, storing, and handling drone batteries. Always use the recommended charger and avoid overcharging or discharging batteries. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Several factors influence a drone’s flight time. These include weather conditions (wind, temperature), drone load (camera, accessories), and flight style (aggressive maneuvers reduce flight time).
Drone Flight Time Comparison
Flight times vary significantly between drone models. The following table provides a comparison (note: these are illustrative examples and actual flight times may vary).
| Drone Model | Battery Type | Battery Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone A | LiPo 3S | 5000 | 25 |
| Drone B | LiPo 4S | 6000 | 35 |
| Drone C | LiPo 6S | 8000 | 45 |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is essential for maintaining operational readiness. This section covers identifying potential causes and providing solutions for resolving common malfunctions.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions, How to operate a drone
Addressing common drone issues efficiently and safely is critical. Always prioritize safety during troubleshooting. If unsure about a problem, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek professional assistance.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
The following flowchart Artikels a systematic approach to troubleshooting common drone issues.
Problem: Drone won’t power on.
Check battery level. If low, charge the battery. If still not working, check the power switch and connections. If the problem persists, contact support.
Problem: GPS signal lost.
Ensure clear skies and GPS is enabled. Try restarting the drone. If the problem continues, relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
Problem: Motor malfunction.
Inspect the motors for damage. Check for obstructions. If a motor is damaged, replace it. If the problem persists, seek professional repair.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced techniques enhance the creative possibilities of drone operation. This section covers achieving cinematic movements, using waypoints, and employing specialized accessories.
Cinematic Movements and Stabilized Footage
Achieving smooth, cinematic movements requires practice and understanding of the drone’s capabilities. Techniques include slow, deliberate movements, precise camera control, and the use of stabilization features. Practice in a safe, open area is recommended.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight Planning
Waypoints allow for pre-programmed flight paths, enabling complex shots and automated sequences. Planning software and apps simplify the process, creating more efficient and repeatable flights. Ensure you understand the limitations of automated flight and always maintain visual contact with the drone.
Specialized Drone Accessories
Various accessories can enhance drone performance and capabilities. These include ND filters (for reducing light), polarizing filters (for reducing glare), and specialized gimbals for increased stability. Choosing the right accessories depends on your specific needs and shooting style.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. From the meticulous pre-flight checks to the exhilarating experience of capturing stunning aerial footage, this guide has provided a foundation for your drone piloting journey. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect regulations, and continue honing your skills to unlock the full potential of your drone.
Safe flying!
FAQ Resource
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Research models known for ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, execute a safe emergency landing procedure.
Can I fly my drone in the rain?
No, most drones are not waterproof and flying in rain can cause irreparable damage.
How do I obtain necessary permits or licenses for drone operation?
Regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority or government agency to determine the specific permits and licenses required in your area.